)
Introduction
Today’s threat intelligence market is growing at a significantly faster pace than in previous years, from $9.81 billion in 2022 to $11.27 billion in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.9%. Additionally, the threat intelligence market is expected to grow to $19.55 billion in 2027 at a CAGR of 14.8%. These numbers represent a substantial jump over earlier estimates, which projected a CAGR of 8.2% between 2020 and 2025. Several factors are driving this growth, including the ongoing recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russia-Ukraine war, and a growing, increasingly complex attack surface. Companies across industries are increasing investments in threat intelligence solutions to reduce their attack surface exposure, strengthen protection of assets and brand value, and reduce risk.
This report highlights the findings from our recent Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) Survey, in which we spoke to more than 100 CTI practitioners and managers to better understand their organizational threat intelligence objectives. We also discussed the greatest challenges they face in leveraging CTI to strengthen cyber defenses and protect their companies from an attack.
Respondents were primarily from North America (47%) and Europe (30%), with others from LATAM, APAC, Israel, and India. Roughly 68% of respondents were cyber security practitioners, operating as cyber threat analysts, threat hunters and security investigators. Approximately 32% were at management level and above, including CISOs, SOC managers, Chief Risk Officers, Vice Presidents of Technology, security architects, and others.
Key Findings
For both leadership and practitioners, the top objectives for most CTI users are related to:a. Understanding the earliest indications of an organization’s riskb. Identifying compromised credentialsc. Assessing an organization’s threat exposure
In other words, managers and practitioners alike believe that threat intelligence can be an important and effective way to understand where a company’s greatest vulnerabilities lie, an important first step in determining how best to stop an attack before it happens.
2. Threat intelligence practitioners and leaders also share similar top challenges related to data aggregation and recognizing trends, particularly when multiple threat intelligence tools are used. Many respondents pointed to analyst fatigue as an underlying challenge that prevents successful use of CTI when relying on multiple solutions and sources.
3. The number of CTI tools in use at any one organization vary widely – from zero tools to three or more. The results show us that many companies are over-subscribing to threat intelligence which prevents them from capitalizing on its full value. For those with no CTI tool in place, there may be too many undifferentiated choices or a lack of perceived value in CTI. Either way, they risk being the victim of a costly cyber attack without meaningful, proactive threat intelligence in their arsenal.
Objectives and Challenges
Top Objectives for CTI Users
The main objectives of CTI tools are similar among managers and practitioners: expose imminent threats to the organization preemptively (60% for managers; 52% for practitioners), identify leaked employee credentials (63% for managers; 46% for practitioners), and assess the organization’s threat exposure and monitor discovered assets across the clear, deep and dark web (43% for both managers and practitioners).
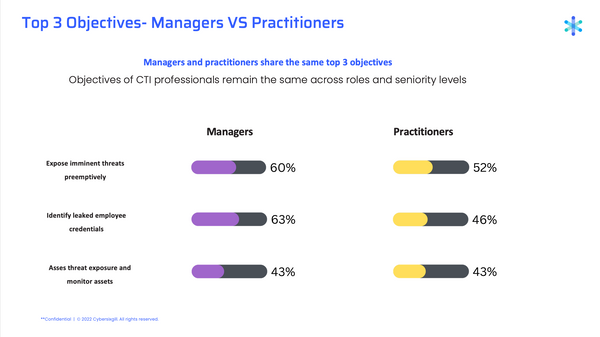 This marks a significant change in activity from our 2021 report, in which respondents cited fraud detection and prevention as their main objective (53%), followed by threat detection (41%) and vulnerability prioritization/management (41%). Clearly, security activities are becoming more proactive, focusing resources on breach prevention by applying threat intelligence to attack surface management solutions.
This marks a significant change in activity from our 2021 report, in which respondents cited fraud detection and prevention as their main objective (53%), followed by threat detection (41%) and vulnerability prioritization/management (41%). Clearly, security activities are becoming more proactive, focusing resources on breach prevention by applying threat intelligence to attack surface management solutions.
Top Challenges for CTI Users
Managers and practitioners also share the same top-level challenges when it comes to using CTI tools: gaining access to relevant sources (30% for managers; 46% for practitioners), identifying relevant intel across large amounts of data (47% for managers; 43% for practitioners), and aggregating intelligence from different sources to gain a complete understanding of overall organizational risk (43% for managers; 40% for practitioners).
 These numbers represent a slight change from what was reported in our Cyber Threat Intelligence Survey, April 2021. In that report, CISOs identified their top three challenges as compliance and regulations (60%), professional knowledge gaps (41%), and hackers (39%).
These numbers represent a slight change from what was reported in our Cyber Threat Intelligence Survey, April 2021. In that report, CISOs identified their top three challenges as compliance and regulations (60%), professional knowledge gaps (41%), and hackers (39%).
In looking beyond the top 3 challenges, managers were equally concerned with scanning and discovering assets (30% vs. 16% for practitioners) and taking down suspicious websites (30% vs. 16% for practitioners), while practitioners were more concerned with gaining access to sources (46% vs. 30% for managers).
Important Tasks and Satisfaction with CTI Tools
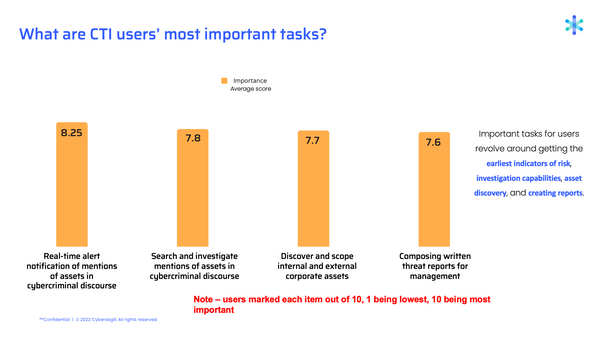
We asked users to rank the importance of 11 tasks to their work on a scale of 1-10, with 1 being least important and 10 being most important. We also asked them to rate how satisfied they are with their current CTI tools when it comes to performing those tasks. The gap between the scores shows us where users are satisfied with their current CTI solutions and where there is room for improvement.
Most Important Tasks
Tasks with the greatest level of importance involve accessing the earliest indicators of risk, investigation capabilities, asset discovery, and creating reports.
 Satisfaction with CTI Tools
Satisfaction with CTI Tools
When it comes to the two most important tasks as identified by users – receiving real-time alert notification of assets mentioned in cybercriminal discourse, and the search and investigation of assets mentioned in cybercriminal discourse – user satisfaction varied by the CTI tool being used. In both instances, Cybersixgill is rated highest by users who both use the solution exclusively and those who use it in combination with other tools.
Number of CTI Tools Used
Roughly half of respondents stated a reliance on a single CTI tool, 13% of whom said they rely only on free OSINT tools or their own internal resources. Nearly 40% said they use more than one threat intelligence solution, half of whom said they use three or more. Surprisingly, 10% of respondents said they have no CTI tool in use.
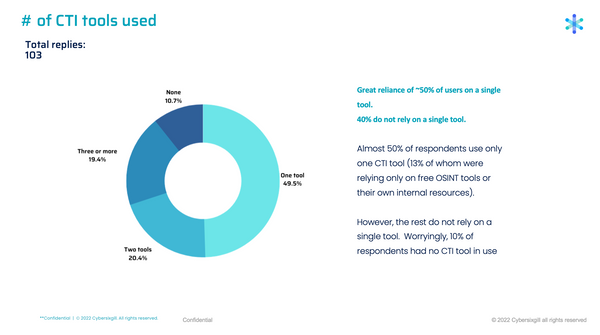 These numbers tell us a few things. For the 10% who said they don’t use CTI at all, as well as for the 13% who use internal resources or free OSINT tools, we see a need for a clearer value proposition in the industry, as well as more differentiation among available solutions. For those who use multiple tools, it seems they may not be getting the expected value from a single solution, which leads to investment in other tools. Too many CTI solutions can create an overwhelming amount of data, which can lead to analyst burnout. In fact, 63% of respondents who use 1 or 2 CTI tools cited gaining access to relevant sources as a main challenge, while 60% of those using 3 or more tools said analyst fatigue is an issue.
These numbers tell us a few things. For the 10% who said they don’t use CTI at all, as well as for the 13% who use internal resources or free OSINT tools, we see a need for a clearer value proposition in the industry, as well as more differentiation among available solutions. For those who use multiple tools, it seems they may not be getting the expected value from a single solution, which leads to investment in other tools. Too many CTI solutions can create an overwhelming amount of data, which can lead to analyst burnout. In fact, 63% of respondents who use 1 or 2 CTI tools cited gaining access to relevant sources as a main challenge, while 60% of those using 3 or more tools said analyst fatigue is an issue.
How Cybersixgill Measures Up
Interestingly, Cybersixgill users fall largely in the group of respondents who said they use only one CTI tool, which indicates that our proactive dark web threat intelligence provides the most comprehensive value over other CTI vendors.
 Among respondents who don’t use Cybersixgill, key issues they identified were greater alert fatigue, more time spent creating reports, and challenges with prioritizing CVEs.
Among respondents who don’t use Cybersixgill, key issues they identified were greater alert fatigue, more time spent creating reports, and challenges with prioritizing CVEs.
Ultimately, Cybersixgill users benefit in a few key ways that users of other CTI tools don’t:
They’re able to rely solely on the tool or use it in combination with one other tools.
The major CTI challenges identified in the survey are less of a struggle for them.
They experience greater satisfaction when it comes to conducting their main tasks.
Summary
Our findings reveal that managers and practitioners shared the same objectives for use of CTI, and also identified similar top challenges in today’s cyber landscape. As technology and threat intelligence capabilities have progressed over the years, the defensive strategies of identifying and resolving a breach which heavily featured in the past, are transforming to more proactive strategies. Organizations are now seeking to gain full visibility of their assets and attack surface exposure, continuously monitoring it with threat intelligence from the clear, deep and dark web to minimize the risk of a breach.
From talking with those on the front lines of defense, it’s clear that users value CTI as a critical weapon for strengthening their security posture and stopping threats before they turn into an attack. Yet not all CTI tools are equal. Satisfaction in respondents’ ability to accomplish their main tasks varied, depending on which tool (or combination of tools) they’re using. It is therefore advisable for security practitioners to regularly re-think their threat intelligence vendors, to ensure access to the most comprehensive, relevant and real-time insights whilst simultaneously consolidating their supply chain.
Download the full report here.
About Cybersixgill
Cybersixgill brings agility to cyber defense, with fully autonomous threat intelligence solutions to help organizations proactively detect and protect against phishing, data leaks, fraud, malware, and vulnerability exploitation - enhancing cyber resilience and minimizing risk exposure in real-time. Cybersixgill’s proprietary algorithms extract data from a wide range of sources, including content from limited-access deep and dark web forums, underground markets, invite-only messaging groups, code repositories, paste sites and clear web platforms, as well as an unparalleled archive of indexed, searchable historical data from as early as the
1990s. This data is processed, correlated and enriched with machine learning techniques to create profiles and patterns of malicious threat actors and their peer networks delivering critical insight into the nature, source and context of each threat.
Our extensive body of threat intelligence data can be consumed through various solution offerings and integrations, each addressing critical customer pain points and use cases.
Learn more at www.cybersixgill.com
Cybersixgill automatically aggregates data leaks and alerts customers in real time.
)
)
)
)